LiquidlAbs
- Year2012
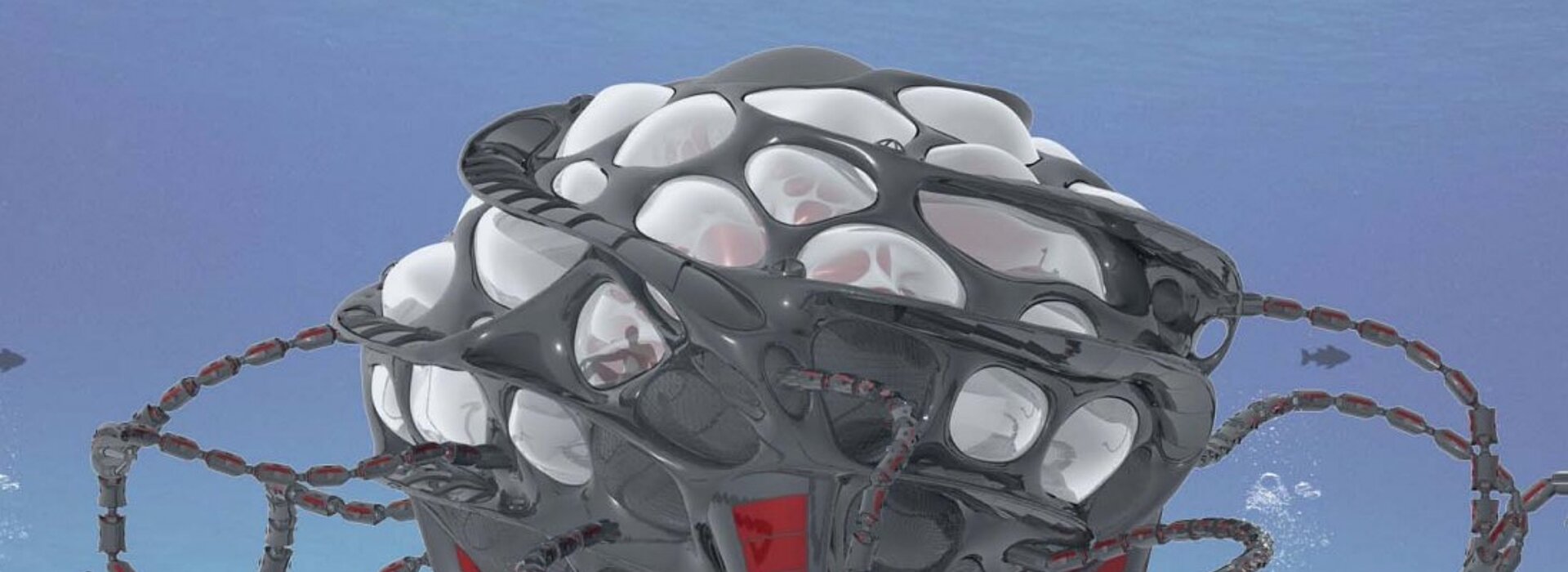
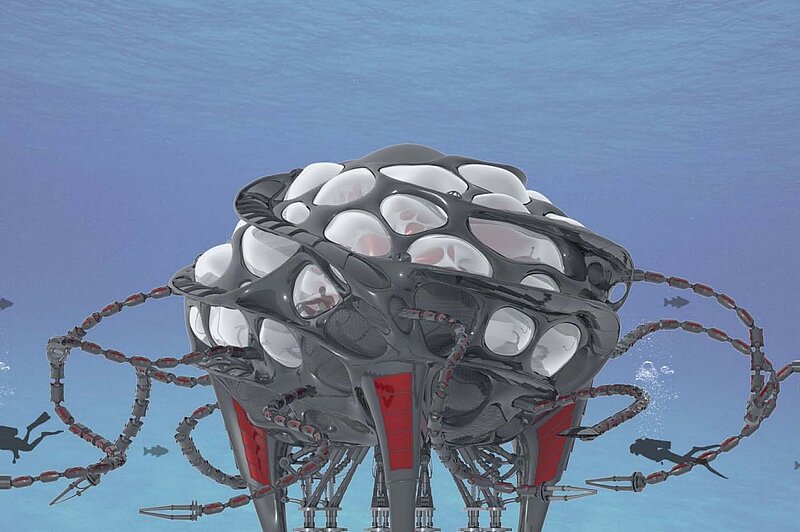
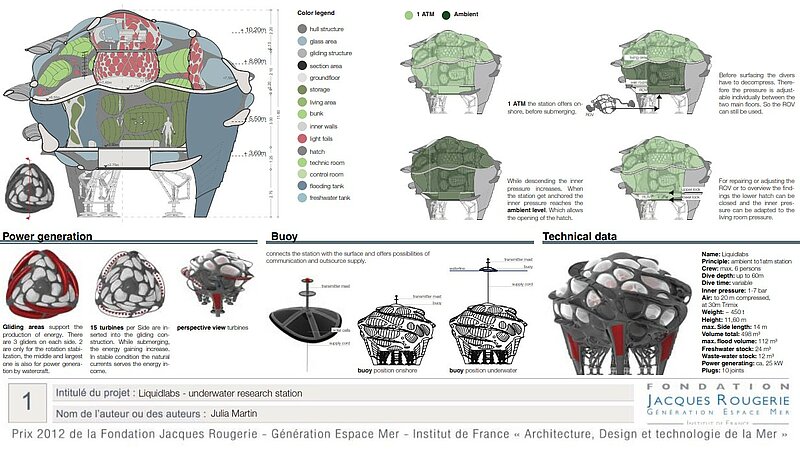
Liquidlabs design is inspired by the shape of diatom structures. The station has no active drive, to be as minimal invasive to its environment as possible. Additionally there is no active drive to avoid disturbances by vibration or noise.
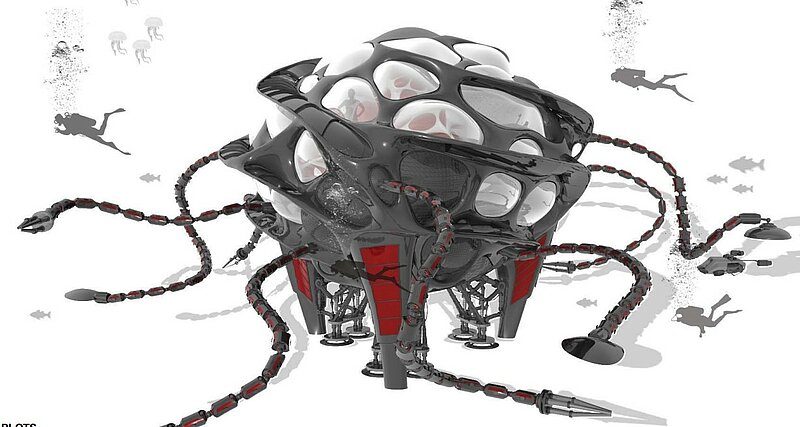
The station is dedicated to professional groups like: archeologists, biologists, astronauts or interested persons. When explorers head for a mission the station gets delivered via “moon pool” ship or cargo airship.
The submerging point can be detected by GPS. By sonar the seabed gets discovered and analyzed to its character.
Depending on what kind of seabed you want to anchor the station offers 3 different possibilities: Spikes, vacuum footing and top row anchors. Depending on the mission goal the devices on the station can be changed. New devices can be delivered by ship and assembled later underwater.
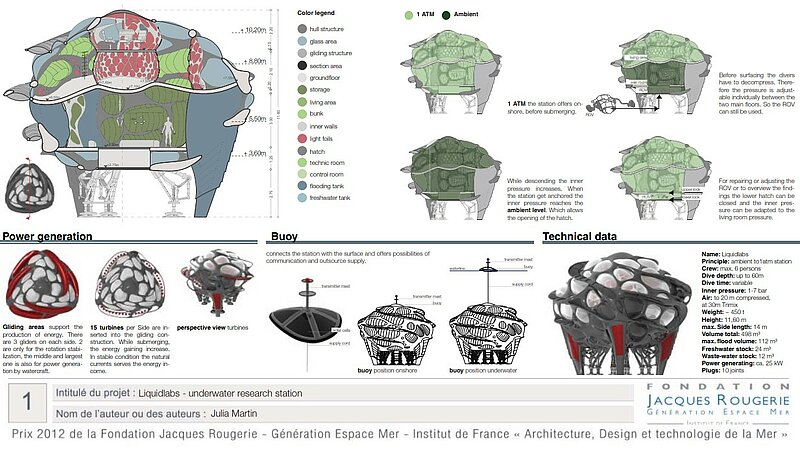
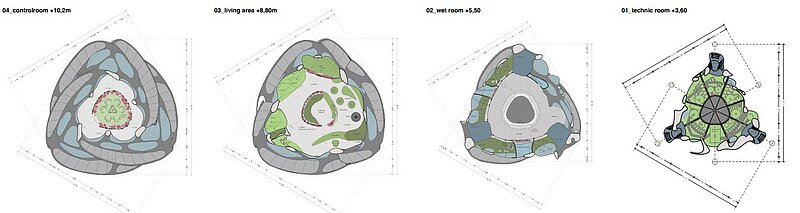
On shore the crew enters the station from the bottom and take seat in the control room while submerging. Through the contact with water the blades in the lower area open up and the station gets flooded. By this process the rotation of the station gets started.
To get stable conditions its important to charge the station steady, also the ballast tanks/fresh water store are in a symmetric order to get an even weight distribution. The hull construction is a double hull system, it can be optionally flooded, in reason of cooling with depth water.
When the station get submerged, the inner pressure is adjusting to its environment. The station rotates around its own axis while submerging, this principle makes it more stable against side currents.