Station gaia Earth Away from Earth
- Year2015
- LocationSpace
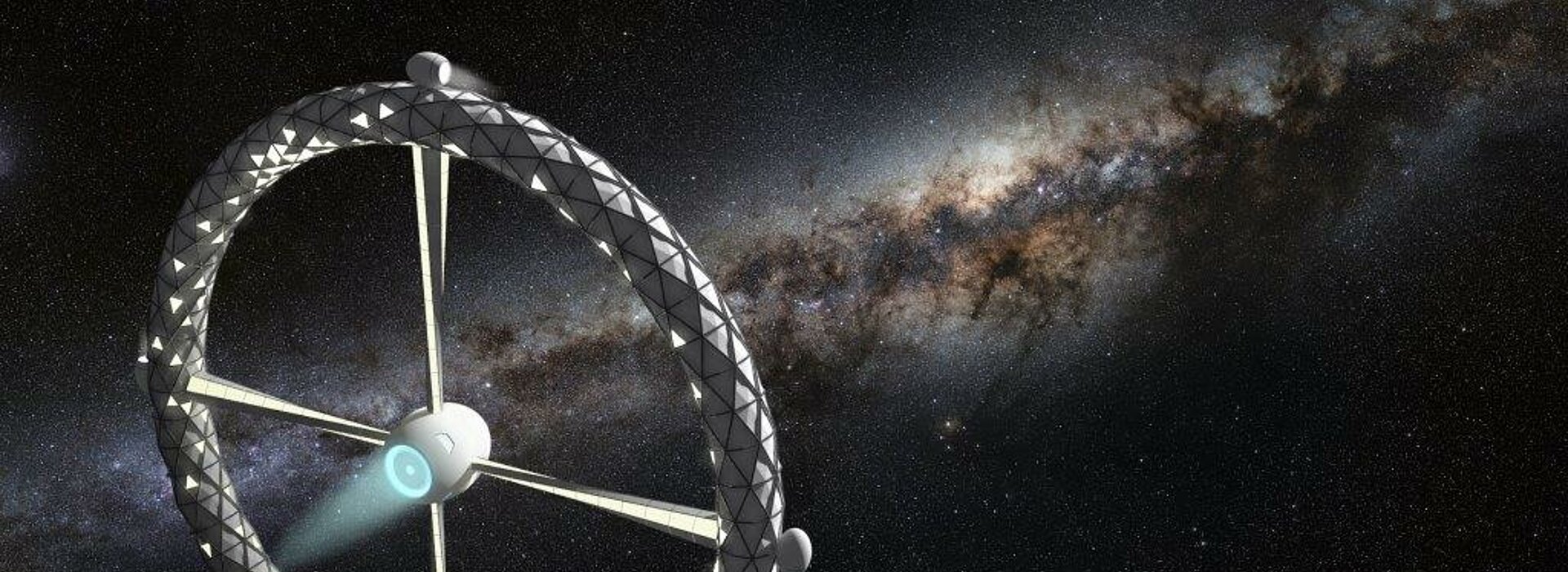
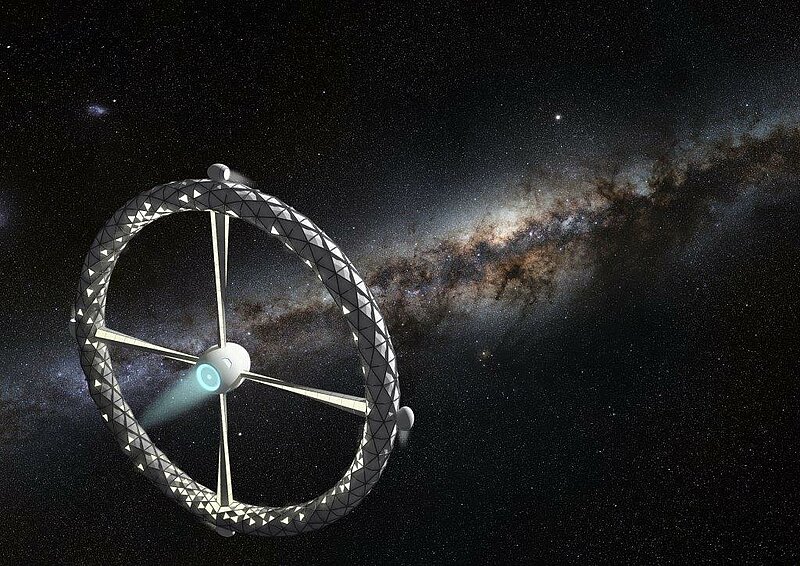
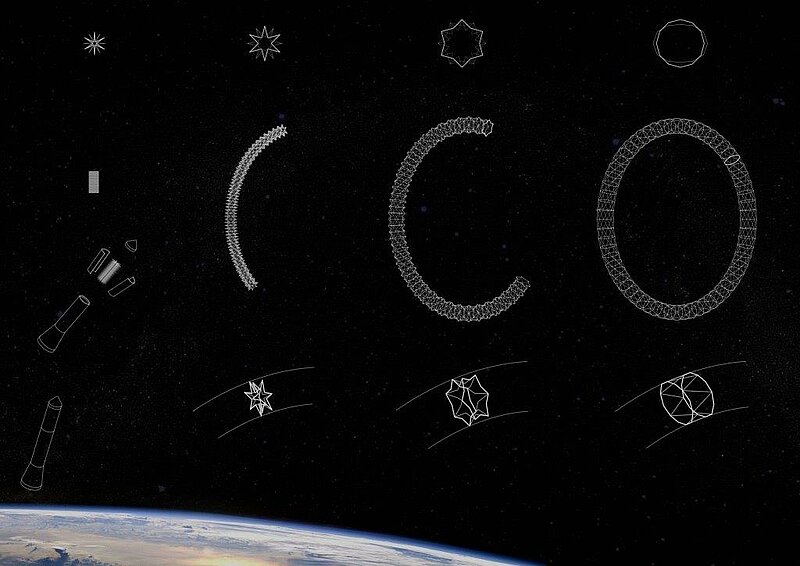
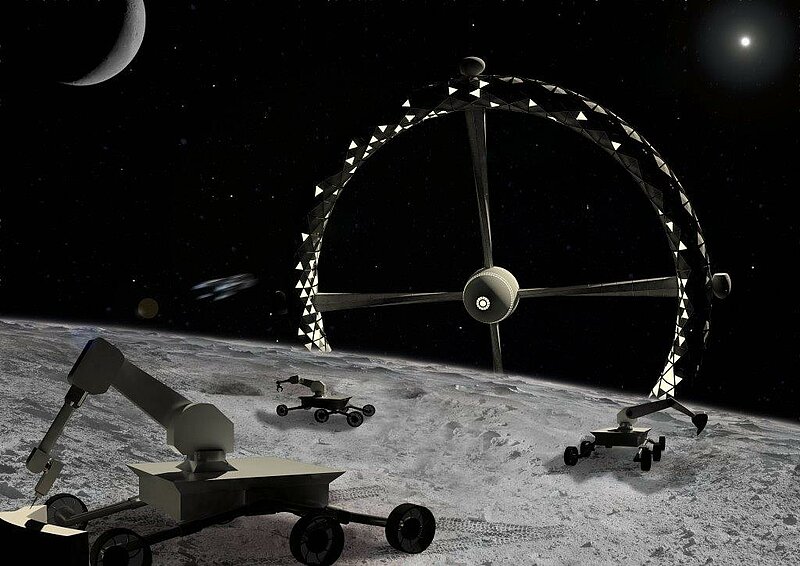
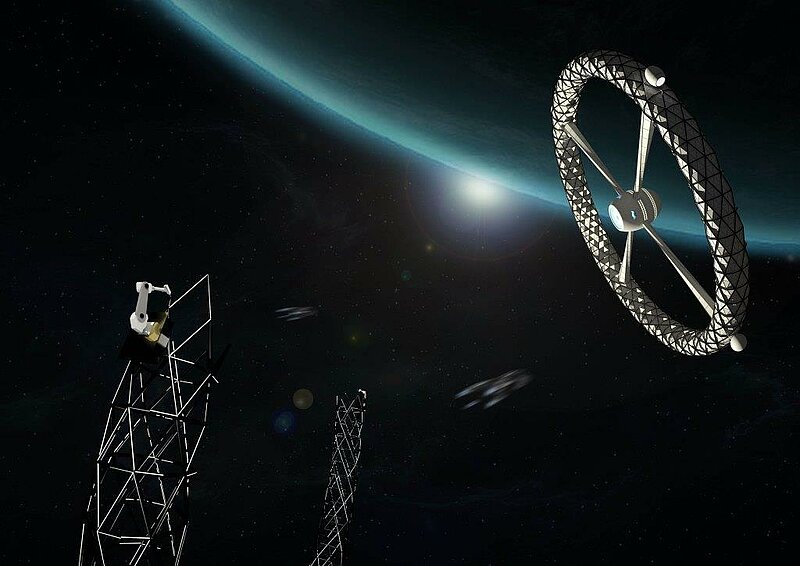
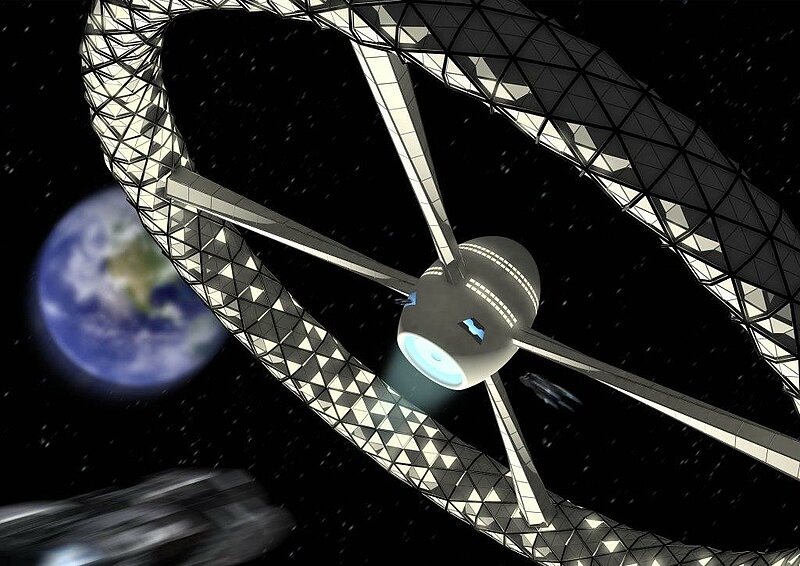
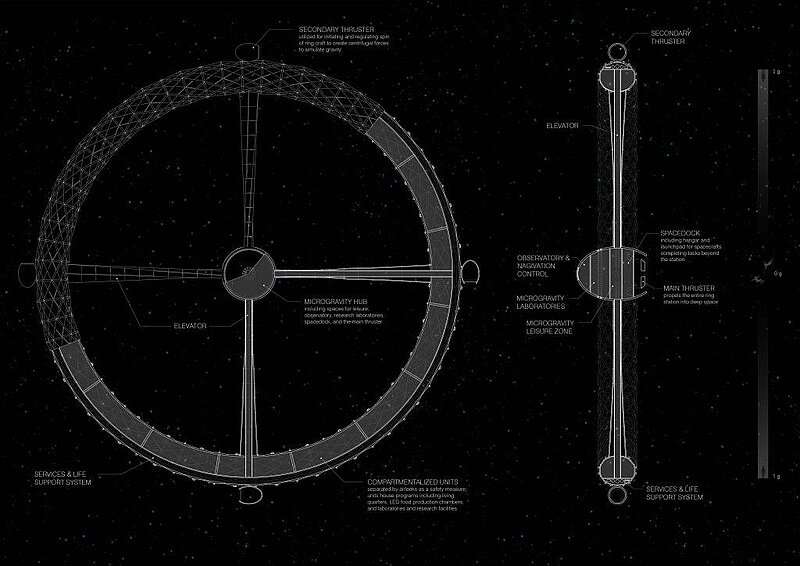
Space exploration today has achieved manned stations orbiting Earth and probes reaching the Kuiper belt, but the extent of our exploration so far is only a miniscule fragment of our infinite universe. Station Gaia will bring the first human colony past the Kuiper belt and into deep space, exploring other stars and galaxies far beyond our own. With Alpha Centauri, the closest star to our Sun, being more than 4 light years away, a deep space expedition denotes a journey beyond the human time scale it is a mission which will extend past numerous generations. While current space stations rely on the constant resupply of materials from human's home planet, a deep space station must detach from the umbilical cord of Mother Earth, and find alternate means to achieve self-sustainment. Station Gaia features a centrifugal habitable ring to simulate the gravitational conditions required to maintain human health and plant growth. Its expandable exoskeleton significantly reduces the size of its payload bay during rocket launch. The inflated interior is compartmentalized into units enclosing living and leisure quarters, food production chambers with LED growth lights, and laboratories and research facilities for the continuing study of our universe. Station Gaia will also conduct expedition to harvest raw materials from space objects along its trajectory. Substances such as methane and water found on Kuiper belt objects will be used for fuel and life support supplies for habitants onboard the station. Metals and other materials will also be harnessed to construct additional habitable stations for the expansion of human space colonies in the generations to come. Serving as a base camp for further explorations into deep space, Station Gaia will be the Earth away from Earth.